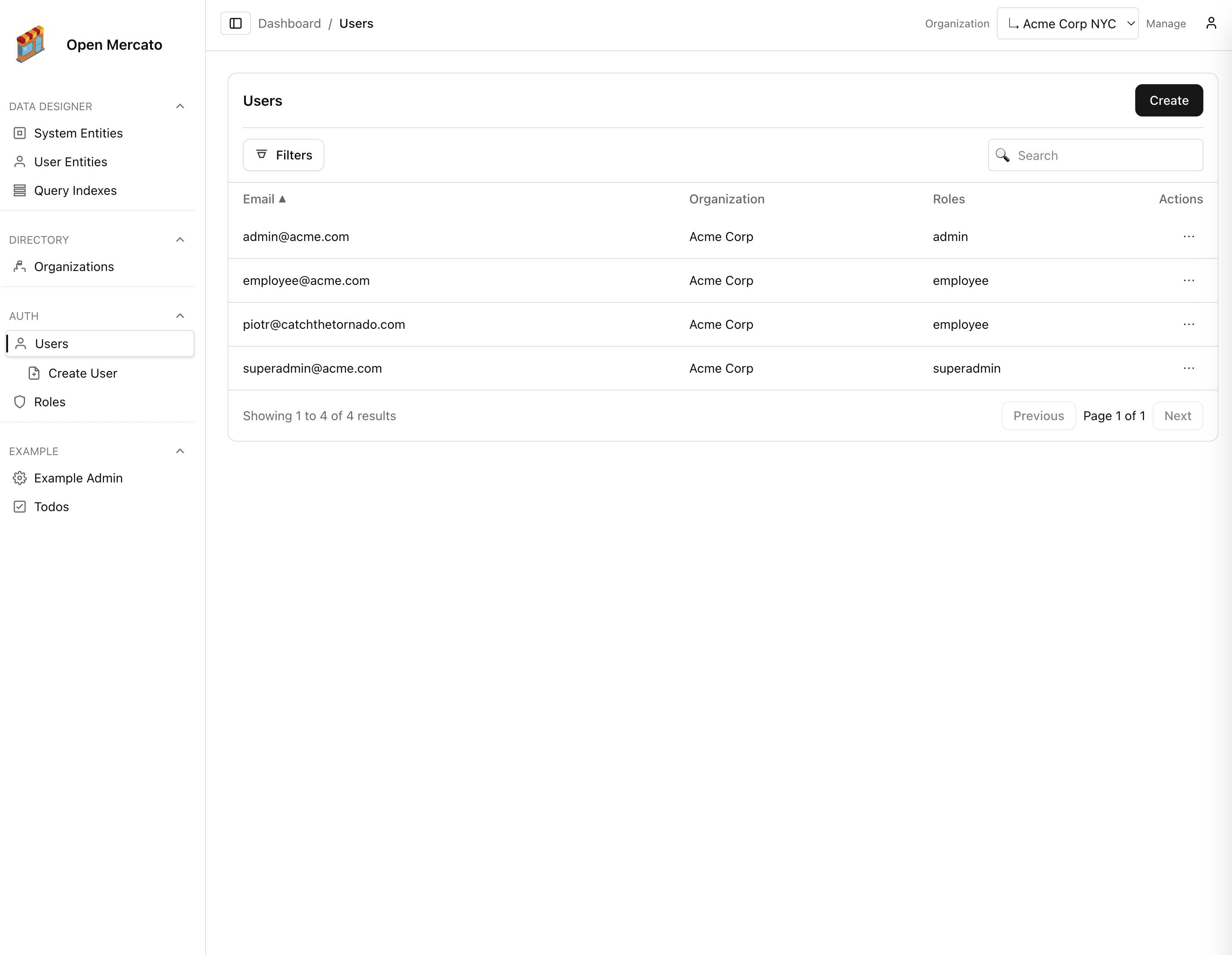
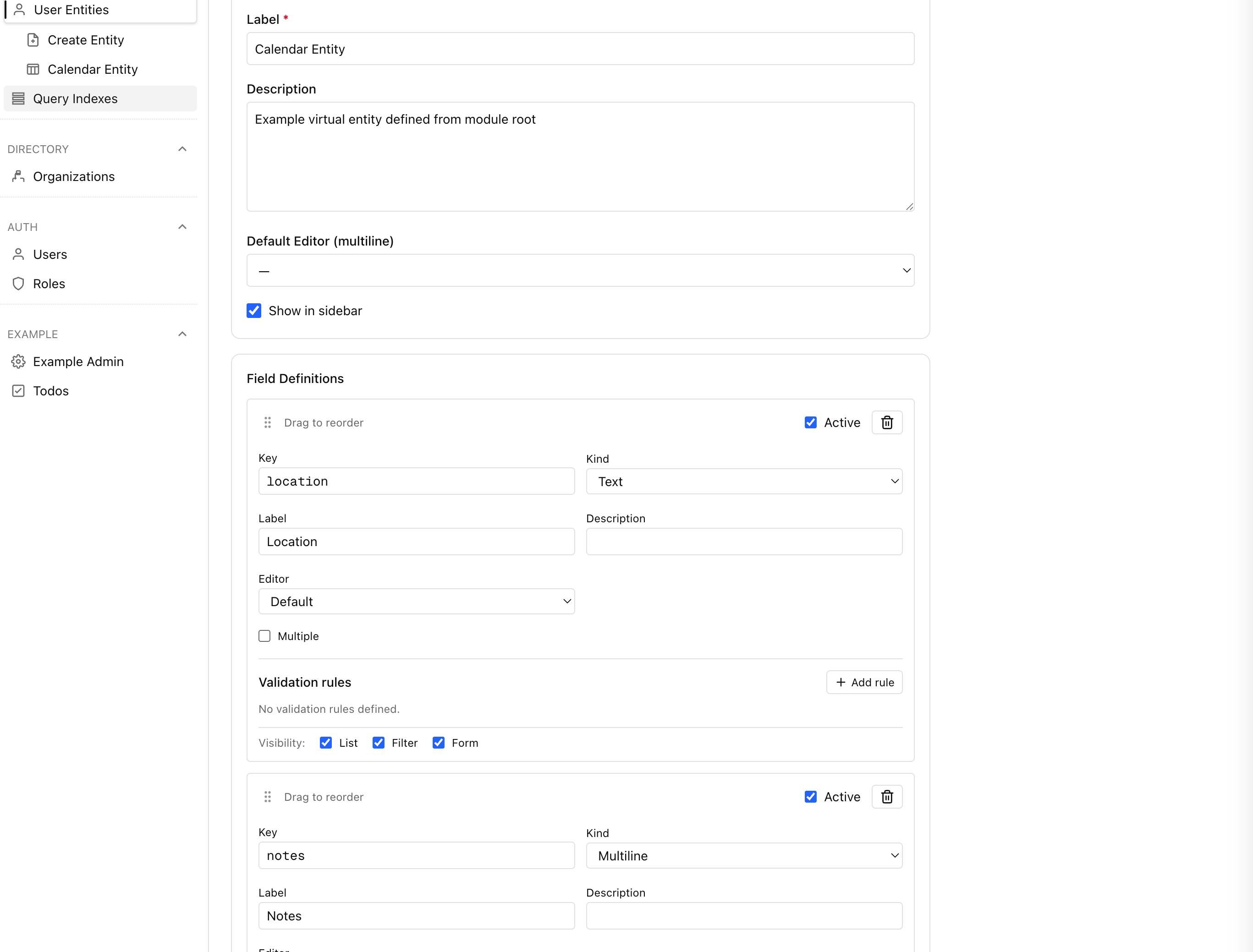
Product Screenshots
Preview core admin experiences. Click any tile to open the full-size capture.
User Guide
Share these guides with operators who need a tour of the admin console and onboarding flows.
User guide overview
Tour the admin dashboard experience and learn where to find core tools.
Dashboard layout
Understand widgets, navigation, and global search on the home page.
Login & authentication
Review the sign-in flow, organization picker, and session persistence.
Resetting access
See how admins and users handle password resets and recovery.
Getting Started
Start with setup, understand the platform capabilities, then dive into user-facing workflows.
Customization Tutorial
Build your first Open Mercato app
Walk through the default application shell, routing overlays, and where to plug in custom modules.
Create your first module
Scaffold the Inventory module and surface its first admin page in the sidebar.
Create the data structures
Model MikroORM entities, validators, and migrations for the Inventory module.
Create the data API
Expose REST endpoints for the Inventory module using the CRUD factory.
Framework
Deep dive into the runtime primitives that power modules, data, and routing.
Dependency injection container
See how the Awilix container wires services per request.
Module authoring & discovery
Understand how modules are discovered, overridden, and registered across the platform.
Routes and pages
Configure frontend and backend routes with metadata-driven auth and navigation.
Entities and migrations
Structure MikroORM entities per module and keep migrations tenant-safe.