Extend users with custom fields
Need to capture extra context about each user? Open Mercato lets you extend the core auth:user entity without editing the module. Define tenant-scoped custom fields, sync them via the Entities CLI, and the admin UI renders the new inputs automatically.
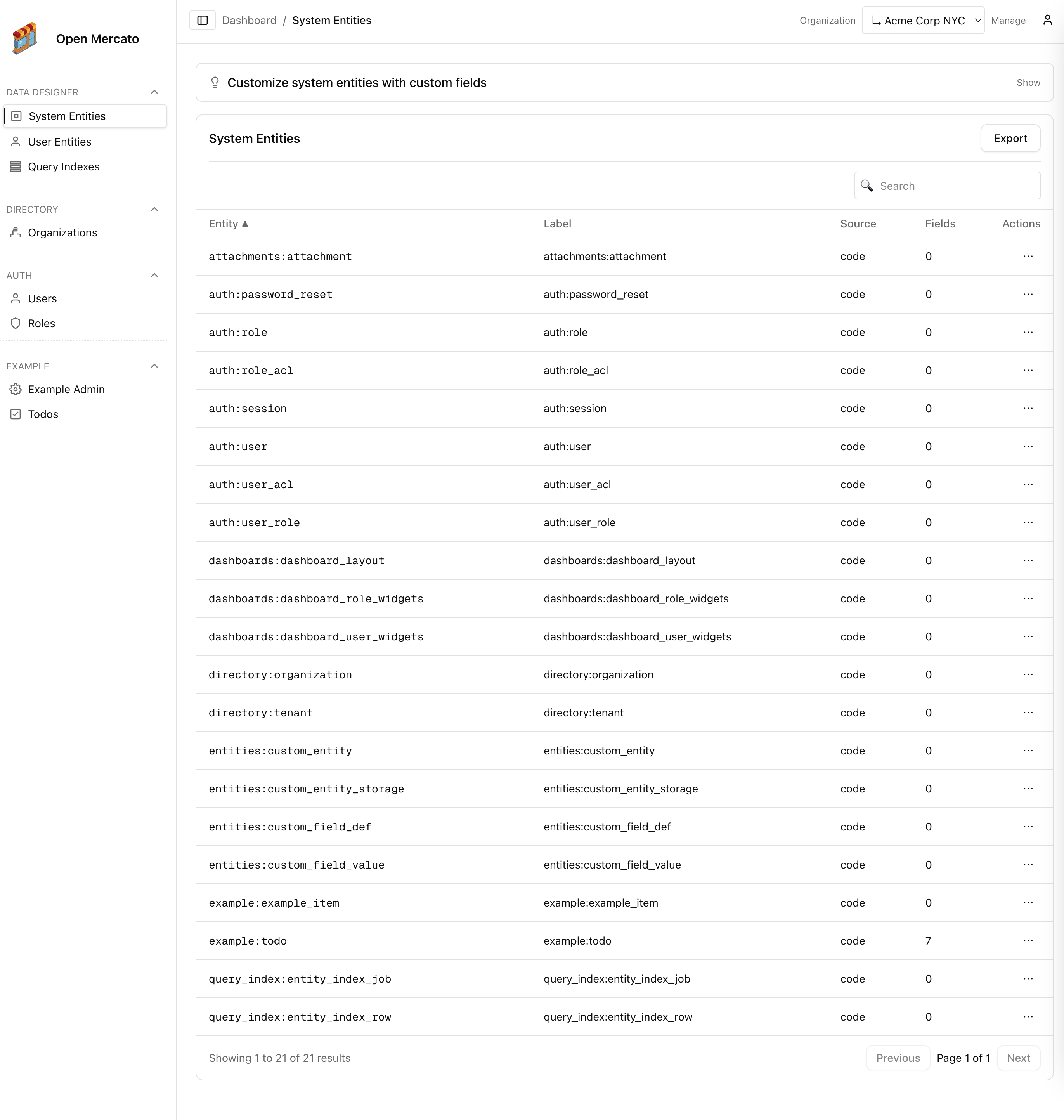
1. Declare the user fields
- Open Backend → Entities → System entities → Users. Add the attributes you need (text, select, relation, etc.) and mark them
formEditableso they are rendered inside CRUD forms. - Prefer keeping field keys snake_case (for example
job_title,language_pref) to stay consistent with API payloads. - If you manage definitions in code, export them from any module
ce.tsand target theauth:userentity id:
import { defineFields, cf, entityId } from '@open-mercato/modules/dsl';
export const entities = [
defineFields(
entityId('auth', 'user'),
[
cf.text('job_title', { label: 'Job title', formEditable: true, filterable: true }),
cf.enum('language_pref', {
label: 'Preferred language',
options: ['en', 'pl', 'es'],
formEditable: true,
}),
],
'compliance'
),
];
- Run
npm run modules:preparewhenever you edit module metadata so generated IDs stay in sync.
2. Apply definitions to the database
Whether you added fields from the UI or code, synchronize them for each tenant:
yarn mercato entities install --tenant <tenantId>
Without --tenant, the CLI processes every tenant plus the global scope. The command is idempotent—rerun it after definition changes or to seed a new environment. See docs/docs/cli/entities-install.mdx for the full option list.
3. CRUD forms pick them up automatically
The user management pages already pass the auth:user entity id to the shared form component:
<CrudForm
fields={fields}
groups={[
{ id: 'details', title: 'Details', column: 1, fields: ['email', 'password', 'organizationId', 'roles'] },
{ id: 'custom', title: 'Custom Data', column: 2, kind: 'customFields' },
]}
entityId={E.auth.user}
/* ... */
/>
The CrudForm component (packages/ui/src/backend/CrudForm.tsx:118) detects the entityId prop, fetches custom field form configs, and appends them to the Custom Data group. No additional wiring is needed; new inputs appear as soon as the CLI sync completes.
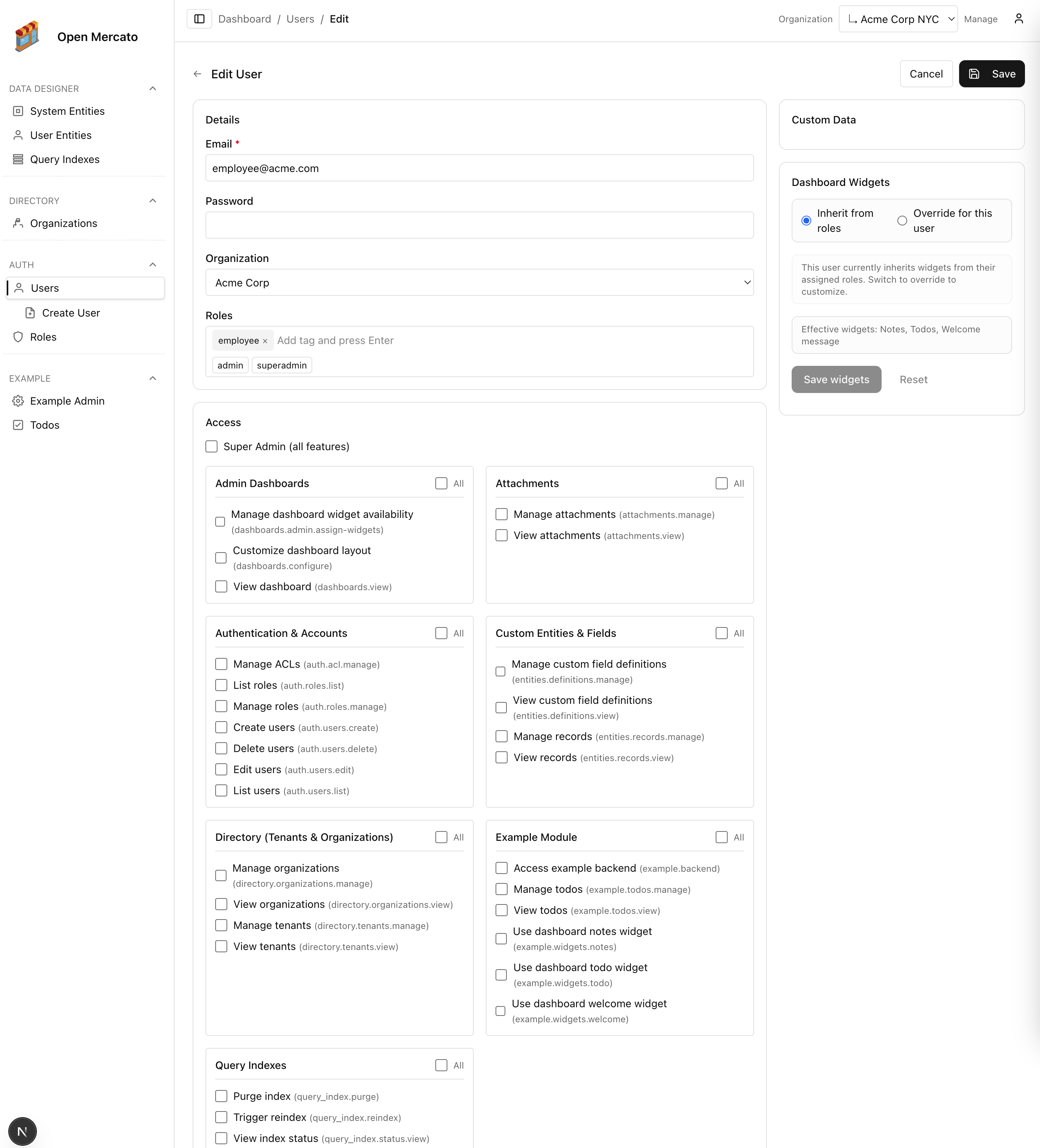
4. APIs persist the new values
The user CRUD API automatically splits payloads into base attributes and custom field values:
const { base, custom } = splitCustomFieldPayload(raw);
/* ... */
await dataEngine.setCustomFields({
entityId: E.auth.user,
recordId: String(entity.id),
organizationId: entity.organizationId ?? null,
tenantId: entity.tenantId ?? null,
values: custom,
});
- POST/PUT handlers accept
cf_<key>properties (for examplecf_job_title) and store them via the shared data engine. - List endpoints and the query engine expose custom fields as
cf:<key>projections, so filters likecf_language_pref=pljust work.
5. Combine profile tables
Some teams split user data between the base auth:user record and auxiliary tables—think HR profiles or staff availability. When those related tables expose their own custom fields, instruct the Query Engine to pull them in by extending the list config (or direct queryEngine.query) with customFieldSources:
const userList = await queryEngine.query(E.auth.user, {
tenantId,
includeCustomFields: true,
fields: ['id', 'email', 'cf:job_title', 'cf:availability_notes'],
customFieldSources: [
{
entityId: E.hr.user_profile,
table: 'hr_user_profiles',
alias: 'hr_profile',
recordIdColumn: 'id',
join: { fromField: 'id', toField: 'user_id' },
},
],
})
The engine merges definitions from every listed entity id, deduplicates keys, and aliases the projected values back to cf:<key>. This keeps multi-table models consistent without duplicating custom field plumbing.
Next steps
- Use the Entities CLI options to automate installations during deployments.
- Extend other directory objects the same way—
auth:role,directory:organization, or your own module entities all support the custom field pipeline.